
peta BumiDatar.id
A Lambert conformal conic projection ( LCC) is a conic map projection used for aeronautical charts, portions of the State Plane Coordinate System, and many national and regional mapping systems. It is one of seven projections introduced by Johann Heinrich Lambert in his 1772 publication Anmerkungen und Zusätze zur Entwerfung der Land- und.
PROYEKSI PETA KREASI HANDAL SELARAS
Sistem proyeksi. Dalam hal proyeksi peta dan sistem koordinat yang digunakan, peta topografi memakai proyeksi Lambert Conical Orthometry (LCO), sedangkan peta rupabumi menggunakan proyeksi Universal Transerve Mercator (UTM) .. Penggunaan proyeksi UTM untuk memetakan daerah Indonesia menjadi lebih tepat jika dibandingkan dengan proyeksi kerucut seperti proyeksi LCO.
Conic Projection Lambert, Albers and Polyconic GIS Geography
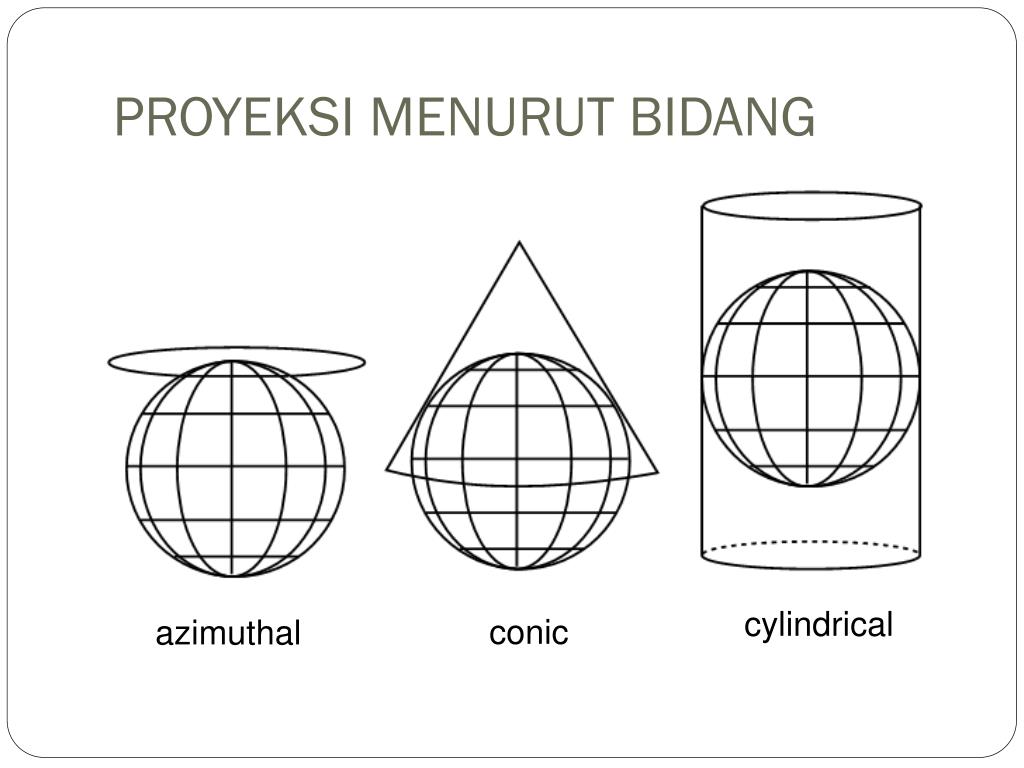
Proyeksi Conical Berdasarkan Peletakan Bidangnya, Orientasi Peta dan Fungsinya, Proyeksi Silinder/Tabung, Prinsip Conform/Konform, Proyeksi Conical/Kerucut, Skala Batang/Grafis/Garis, Proyeksi Azimuthal Berdasarkan Peletakan Bidangnya, Definisi Proyeksi Peta, Komponen Peta,

CV06 Map Projections GIS&T Body of Knowledge
If these lines are a parallel of latitude, as in conical projections, it is called a standard parallel. The central meridian is the meridian to which the globe is rotated before projecting. The central meridian (usually written λ 0) and a parallel of origin (usually written φ 0) are often used to define the origin of the map projection.
Sistem Proyeksi Peta
The polyconic projection is also known as American polyconic or ordinary polyconic projection. The name translates into "many cones," and it is created by lining up an infinite number of cones along the central meridian. This affects the shape of the meridians. Unlike other conic projections, the meridians are curved rather than straight.
PPT P E T A PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3771443
The azimuthal projection intercepts the Earth according to the laws of perspective and plots the traces of light onto a developable surface. When the source of light is placed in different locations, it affects the geometry of the projection. When polar (normal) projections are the center point of the planar projection surface, it results in.
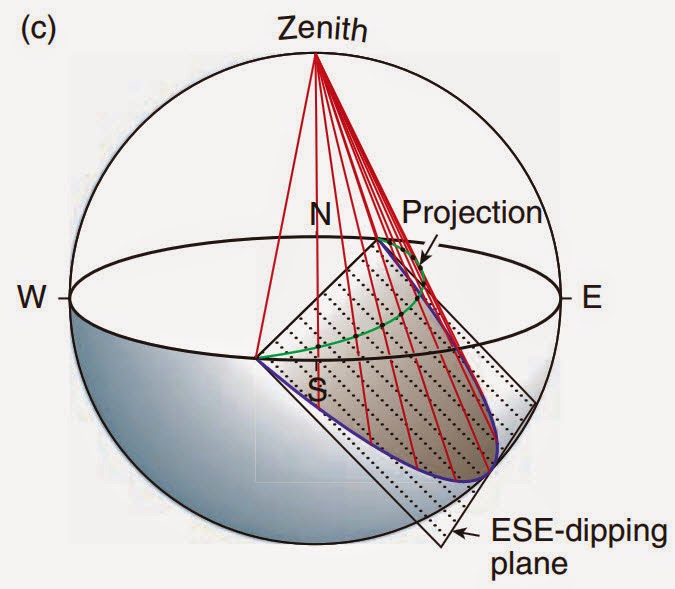
Proyeksi Stereografis dalam Analisis Struktur
Mercator projection of the world between 85°S and 85°N. Note the size comparison of Greenland and Africa. The Mercator projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation. Mercator 1569 world map (Nova et Aucta Orbis Terrae Descriptio ad Usum Navigantium Emendate Accommodata) showing latitudes 66°S to 80°N.. The Mercator projection (/ m ər ˈ k eɪ t ər /) is a conformal cylindrical map.
PPT PROYEKSI, KOORDINAT DAN SKALA PETA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2383483
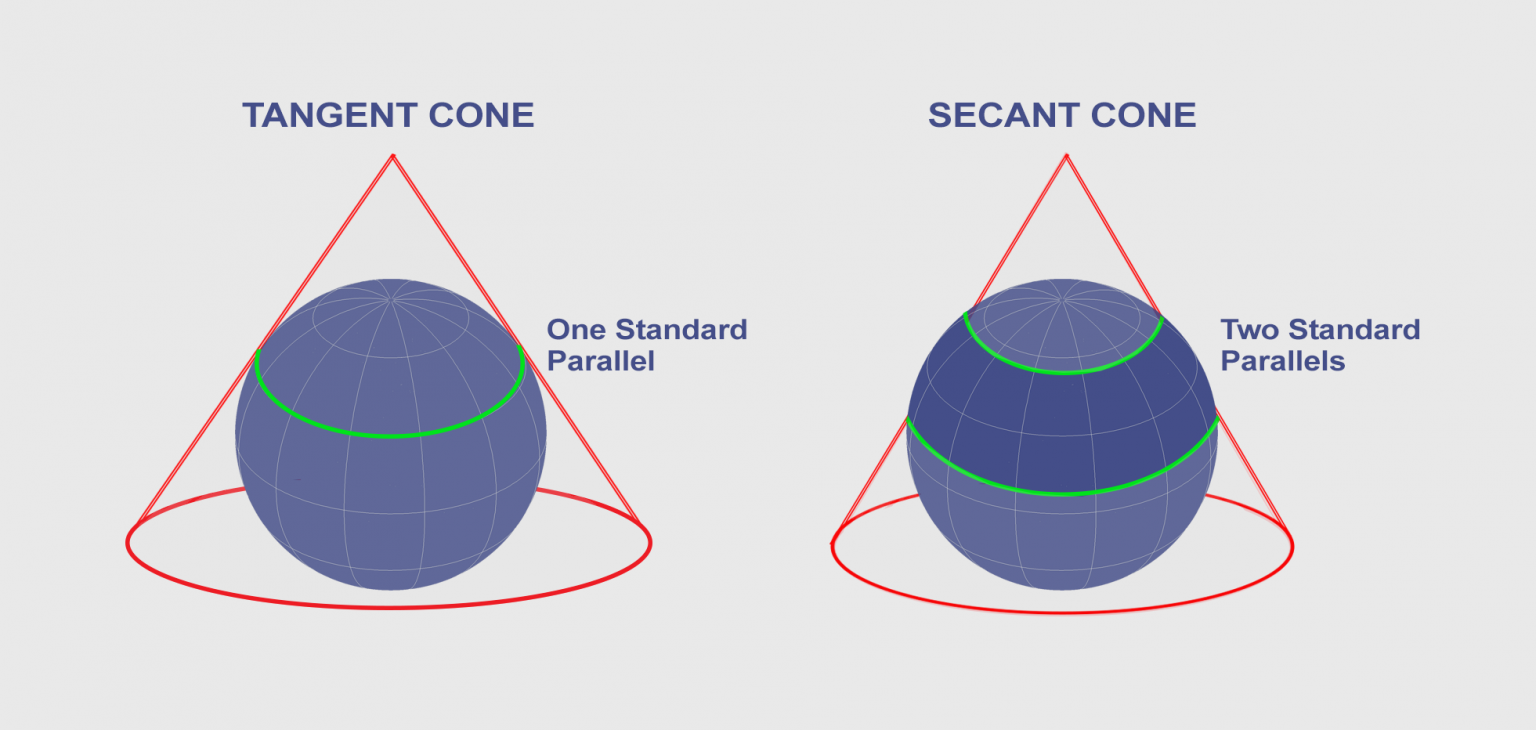
Conic Projections. • A conic projection is formed by bringing a cone into contact with the sphere or the ellipsoid, such as Lambert Conformal conical projection. Conic Projections. Standard parallel of the projection, is the parallel of latitude that tangent the sphere. It is either one tangent or two tangents in the case of the secant.
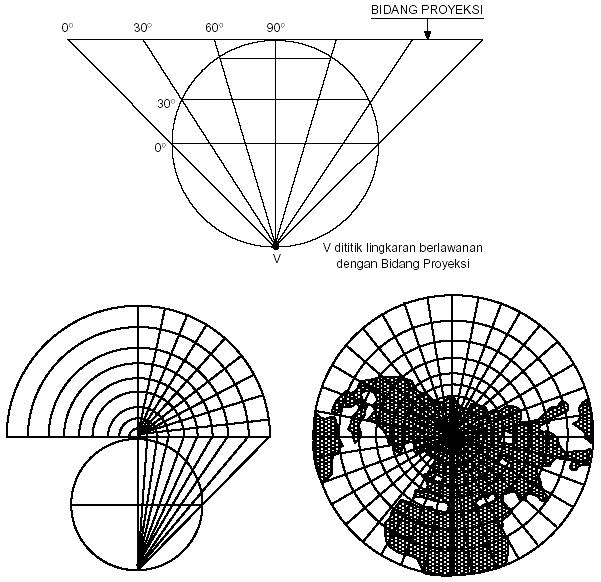
Proyeksi Peta Pembelajaran Geografi
50. Rangkuman 1 Dasar-Dasar Pemetaan. Rangkuman 2 Dasar-Dasar Pemetaan. Rangkuman 3 Dasar-Dasar Pemetaan. Kuis Akhir Dasar-Dasar Pemetaan. 675. 300. Materi pelajaran Geografi untuk SMA Kelas 10 IPS bab Pengetahuan Dasar Pemetaan ⚡️ dengan Dasar-Dasar Pemetaan, bikin belajar mu makin seru dengan video belajar beraminasi dari Ruangbelajar.

PPT PROYEKSI, KOORDINAT DAN SKALA PETA PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2383483
The world on an equidistant conic projection. 15° graticule, standard parallels of 20°N and 60°N. The equidistant conic projection with Tissot's indicatrix of deformation. Standard parallels of 15°N and 45°N. The equidistant conic projection is a conic map projection commonly used for maps of small countries as well as for larger regions.

Simple conical projection with one standard parallel YouTube
Albers Conic Equal Area. This projection, developed by Heinrich C. Albers in 1805, is predominantly used to map regions of large east-west extent, in particular the United States. It is a conic, equal-area projection, in which parallels are unequally spaced arcs of concentric circles, more closely spaced at the north and south edges of the map.
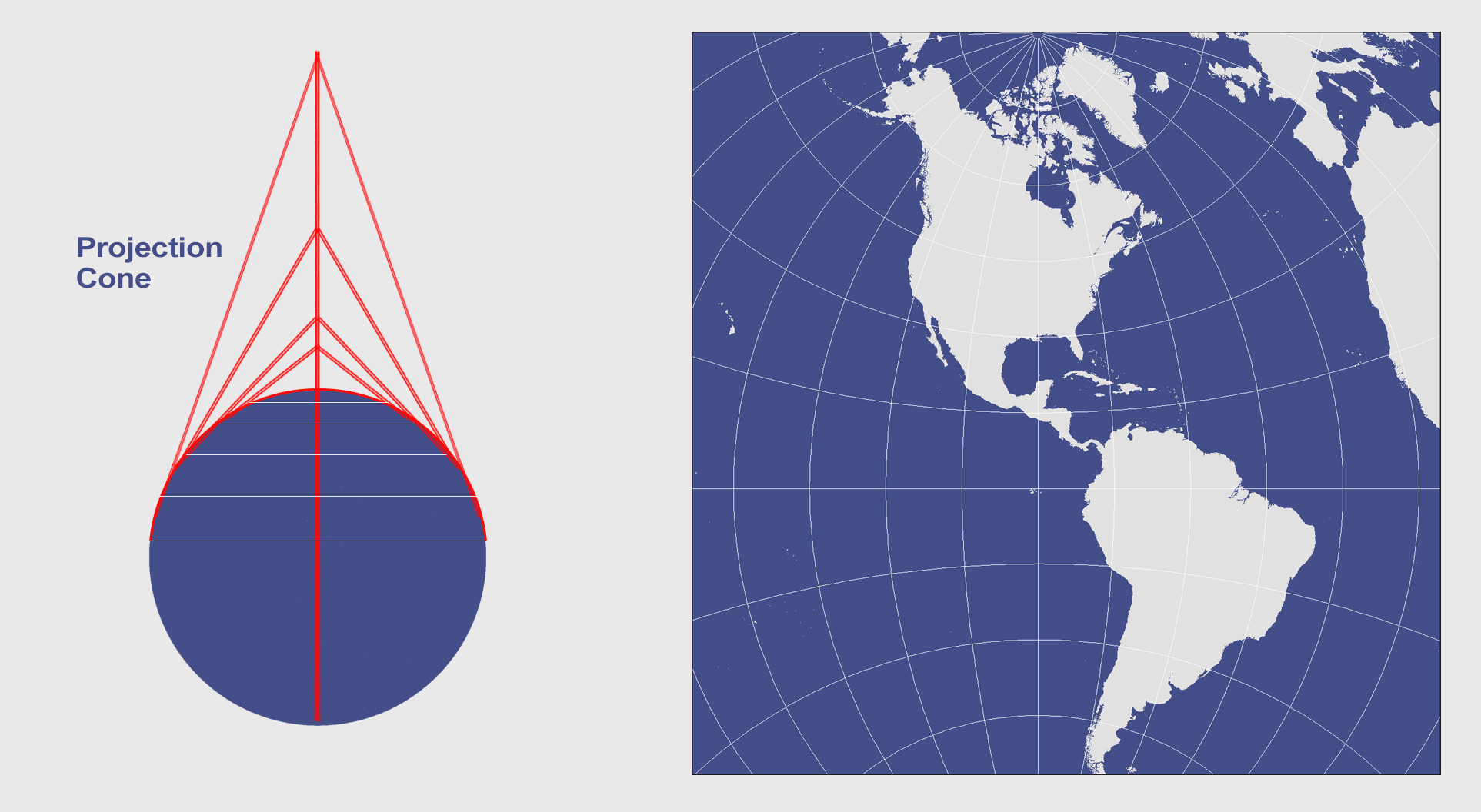
Conic Projection Lambert, Albers and Polyconic GIS Geography
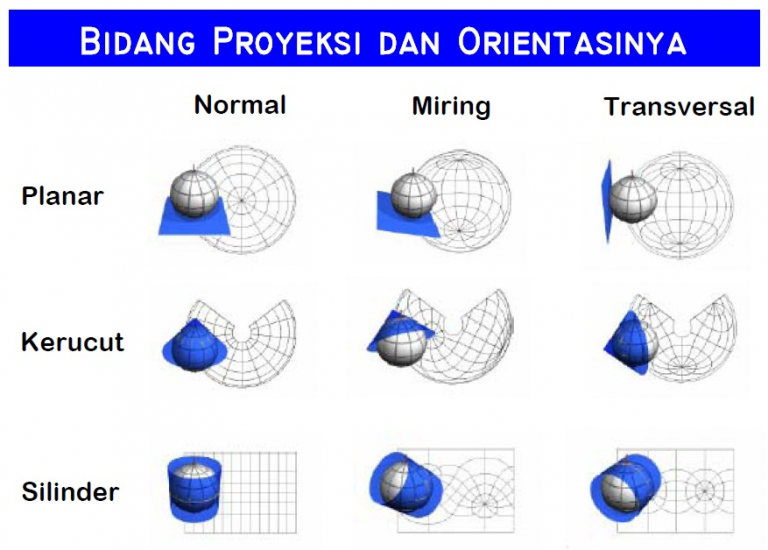
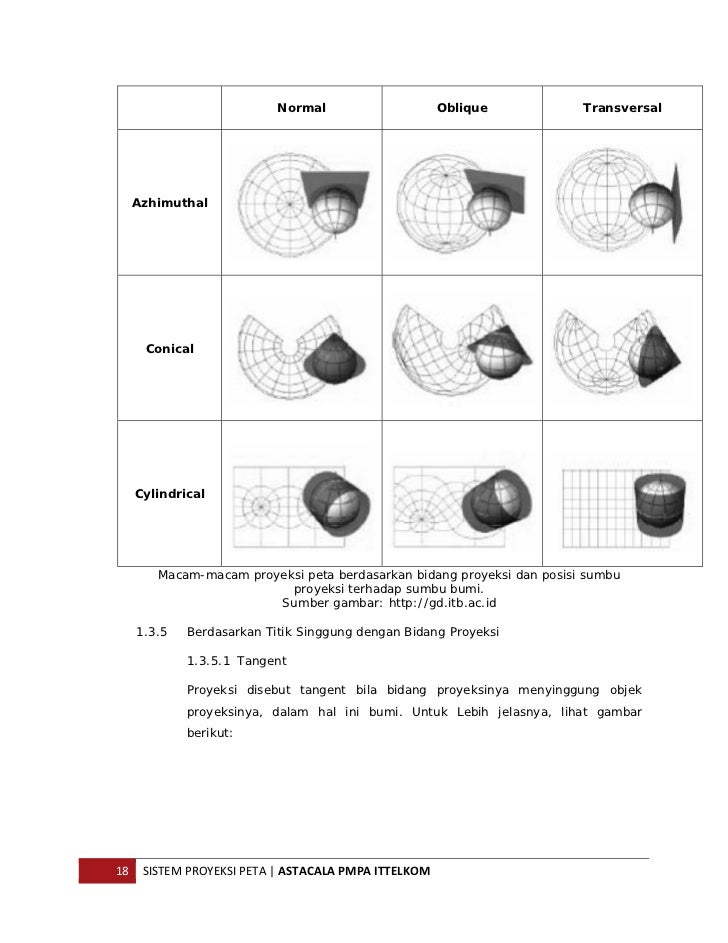
Proyeksi ini cocok memetakan Bumi di daerah khatulistiwa dan tidak cocok jika digunakan untuk bagian wilayah kutub. Proyeksi Peta Berdasarkan Garis Karakter Jenis Proyeksi Peta Berdasarkan Garis Karakter (Dok. Arsip Zenius) Proyeksi Normal; Pada proyeksi normal, garis karakteristik bidang proyeksi berimpitan dengan sumbu bola Bumi. Proyeksi Miring
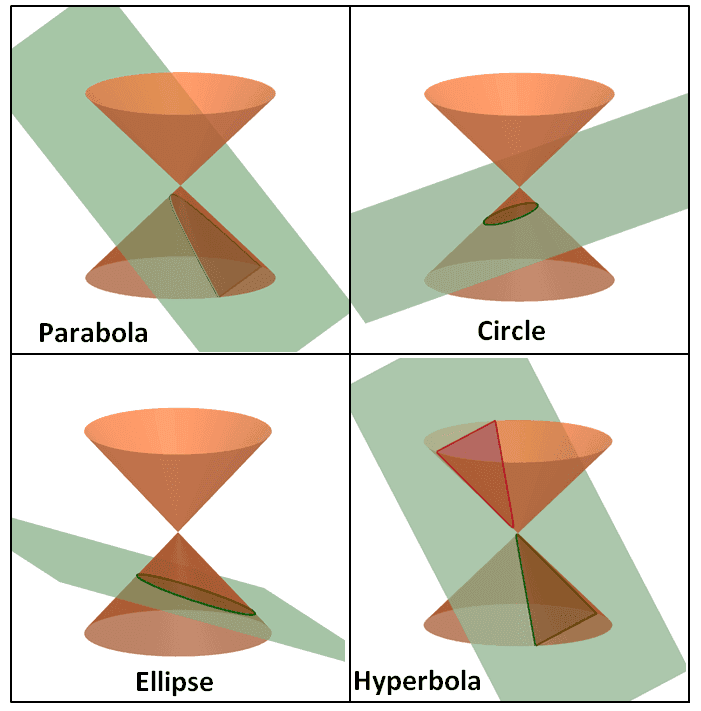
The images above show us how these conic sections or conics are formed when the plane intersects
Conic Projection Examples. When you place a cone on the Earth and unwrap it, this results in a conic projection.. Some of the popular conic projections are the Albers Equal Area Conic and the Lambert Conformal Conic projections.. Both of these types of map projections are well-suited for mapping long east-west regions because distortion is constant along common parallels.
Contoh Gambar Proyeksi Amerika analisis
Proyeksi Peta - Untuk lebih jelasnya mengenai macam-macam proyeksi peta, berikut ulasannya diserta gambarannya.. Proyeksi Kerucut (Conical Projection) Proyeksi Kerucut yaitu pemindahan garisgaris meridian dan paralel dari suatu globe ke sebuah kerucut. Untuk proyeksi normalnya cocok untuk memproyeksikan daerah lintang tengah (miring).

Anwari
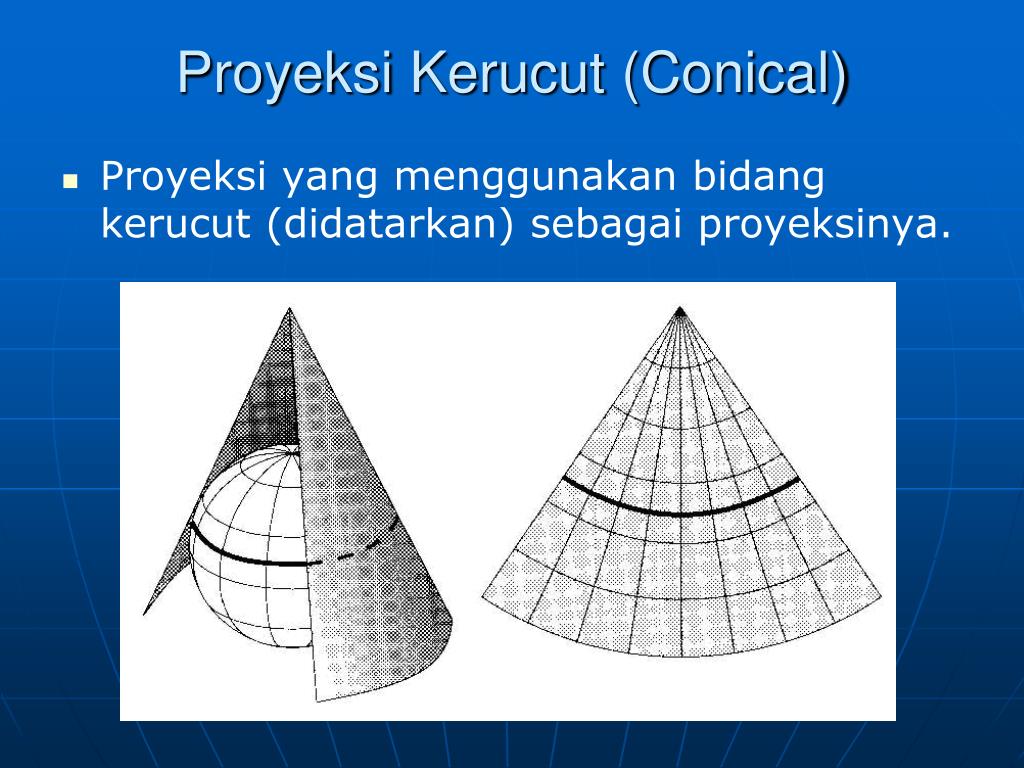
Proyeksi kerucut/conical, menggunakan bidang kerucut sebagai bidang proyeksi. Proyeksi kerucut cocok digunakan untuk memetakan daerah lintang tengah karena bidang proyeksi menyinggung wilayah tersebut. 3. Proyeksi silinder/silindris, menggunakan bidang silinder sebagai bidang proyeksinya. Proyeksi ini punya keunggulan yaitu dapat memetakan.
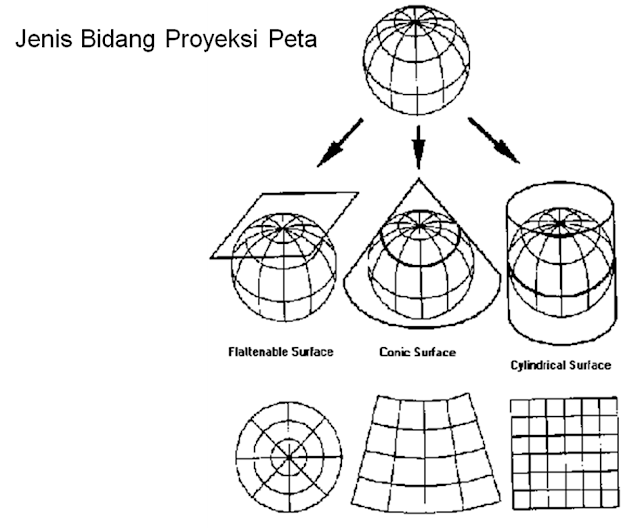
Proyeksi Peta Pembelajaran Geografi
Lambert conical orthomorphic (or conformal conic) projection a line of constant longitude projects into a radial for which 8 = sin ¢ 0 .1 A . (4) Equation (4) follows easily from equations (1), (2) and (3). Differentiating, d 8 = sin ¢ 0 A . (5) Now let P be a point at latitude ¢ on the meridional line through P 0